Wondering if the metaverse is just a fad? While you’re sitting on the sidelines, top brands have arrived at the new e-commerce frontier. Use this guide to plan your entrance into the metaverse and define your e-commerce trajectory for decades.
Inside this article:
What Is Metaverse E-commerce?
Metaverse e-commerce is commerce that takes place in the metaverse. Metaverse e-commerce blends online retail with in-person shopping. It also offers interactive experiences and rich 3D visuals. Metaverse transactions use cryptocurrency and the blockchain.
First, what is the metaverse? The question may seem simple, but the answer changes based on who you ask.
Many experts characterize the metaverse as a natural evolution of today’s internet. Rather than a static, passive experience, the metaverse will be a dynamic, immersive digital space that works seamlessly across platforms and is enhanced by virtual reality, augmented reality (AR), NFTs and other decentralized finance technologies. Key aspects of the metaverse include the new ideas of ownership (including blockchain and NFTs), enabling of a creator economy and utilization of composable technology to develop new approaches to entertainment and customer engagement. As the pieces fall into place over the next decade, the metaverse will become a digital parallel of our everyday lives: everything we do in real life, we will do in the metaverse. As the next organic avenue for retail shopping, it is dependent on the ability of customers to share ideas and collaborate. The metaverse will usher in a new, flourishing digital to support the digital parallels of our real lives, including e-commerce.
You’re not alone if you’re just learning about the metaverse. According to a recent survey by Gartner, consumers today really don’t give it much thought. Only 6 percent of consumers surveyed knew what the metaverse was and felt like they could explain it. Brands, on the other hand, are already staking a claim to create the metaverse e-commerce ecosystem.
What does this new ecosystem look like? In Web 2.0, the typical e-commerce experience feels disconnected from the physicality of in-person shopping. The metaverse will fill that gap: Customers will be able to “move” around a store, try things on, socialize, and complete purchases, all from the comfort of their own homes.
Consider this example: Your avatar is roaming through a virtual store when a product catches your eye. You grab at it, rotate it, and zoom it, easily manipulating it as if you were holding it in your hands. Click on the product, and it might transport you to a user manual, a video, or an instant, interactive comparison chart with a competing product. Maybe this is a virtual-only good, or perhaps it’s a 3D model of a physical product you’d like to buy. In any case, you could always reach out to one of your friends’ avatars to ask their opinion. Does this sound like the best of online shopping combined with the best of physical shopping? That’s the point!

Dedrick Boyd, CEO at TechSparq
Dedrick Boyd, CEO at TechSparq, thinks of metaverse e-commerce as “commerce that takes place in an experience-rich environment using 3D products in extended reality (XR). It offers the ability to communicate audibly and visually in real-time with others without leaving the virtual experience.”
Still, metaverse commerce is in its nascent stages. “Transactional integration is still missing in metaverse commerce,” Boyd points out. “Meaning, customers are pulled out of their immersive experiences and dropped on the static 2D web pages to complete purchasing transactions.”
These issues are simple growing pains, certain to be solved sooner rather than later. If you wait until experts work out metaverse kinks, you’ll be much too late. Just look at the numbers: Acumen Research and Consulting predicts that the global metaverse market size will reach a market value of 1 trillion U.S. dollars by 2030. Importantly, it will grow at an annual rate of .
If you want your brand to be a metaverse success story, you need to experiment and reimagine every dimension of your business. No matter what the metaverse grows into, brands that are too afraid to take the leap will undoubtedly miss out and perhaps even flounder.
Key Takeaways:
- The metaverse will transform traditional e-commerce.
- Metaverse customers will demand personalized, immersive experiences that are visually engaging.
- Metaverse e-commerce promises more profits, lower return rates, and improved customer engagement.
- Major brands in all business sectors have already begun metaverse e-commerce campaigns.
- To prepare for the metaverse, start by partnering with experts in 3D visuals.
What Does the Metaverse Mean for E-commerce?
The metaverse will transform e-commerce. Consumers will want brands to help make their metaverse journey more visually rich and immersive. Plus, transactions will all use cryptocurrency and the blockchain.
Ongun Duman, Marketing and CX Manager at Amazon, points out that businesses that expect their successful Web 2.0 campaigns to work well in Web 3 may be making business-ending assumptions. For Duman, basic customer behavior won’t change, but their standards will.
“Customers’ purchase decisions will still be made by well-informed considerations sensitive to price, product information availability, and ease of experience,” Duman explains. “However, since the metaverse will enable seamless virtual shopping experiences, e-commerce websites will be expected to meet a significantly higher standard by customers. So, though a customer’s basic purchasing decision will not change, brands will be expected to build and create customer journeys in the metaverse instead of simply enabling purchases. Being a key part of customers’ metaverse experience and creating interactive 3D content will be the key to establishing your company in this virtual world.”
How Is E-commerce in the Metaverse Different?
Businesses will use metaverse e-commerce to prioritize personalized, immersive experiences. It will use new payment and ownership methods based on cryptocurrency. These practices will lead to higher profits, better customer insight, and lower return rates.
Boyd of TechSparq believes the major difference between traditional and metaverse e-commerce is the integration of emotional, human values. Boyd says, “Metaverse e-commerce will bridge the gap between a product landing page and human interaction. Metaverse commerce provides customization for a highly personalized experience while diving deeper into the brand ecosystem, whereas traditional e-commerce stops at product recommendations and discounts.”
Boyd thinks the metaverse will also support community engagement. He continues, “Metaverse commerce will allow for customer interaction between brands, products, and other customers while shopping, and will thereby foster community engagement. In contrast, 2D product pages and traditional e-commerce create a solitary shopping experience. “
Still, in 2022, we are straddling the border between traditional and metaverse e-commerce. Metaverse e-commerce largely caters to a generation of digital natives comfortable with the digital goods economy. As they come of age and have more buying power, brands will mirror their habits, creating robust, real-world commerce experiences that businesses will duplicate in the metaverse. In contrast, today’s metaverse e-commerce represents a unique merging of changing practices while still holding onto internet commerce. But our collective grip on internet e-commerce will loosen as the technology enabling the metaverse improves, and its predicted global adoption becomes a reality.
Here’s a list of some of the significant ways that metaverse differs from traditional e-commerce:
- Immersive gamification and iCommerce
Brands venturing into the metaverse have converged on a common tactic: creating revenue streams from experiences rather than products. For example, to celebrate its 200th birthday, luxury brand Louis Vuitton created an interactive game in which players move through otherworldly virtual environments, collecting candles – 200, to be exact, that span Lois Vuitton’s collaborations, trivia, and highlights. These include 30 NFTs (non-fungible tokens). The game doesn’t generate immediate profits, but customers walk away from the experience with positive, deepened feelings toward the brand and feel excited to explore new products. The lucky users who found NFTs gain a heightened sense of exclusivity. Likewise, Samsung’s new addition to Decentraland lets “guests embark on a journey where they can explore the experiences unlocked with Samsung technology.” Notice the company emphasizes experiences and doesn’t peddle one specific product. This new interactive, immersive commerce has a catchy nickname: “iCommerce.”Automaker Nissan has digitally recreated its glitzy Nissan Crossing showroom in Tokyo to feature its electric vehicles, the Ariya and the Sakura. It introduced the VR showroom using the VRChat platform with an invitation-only event. The most innovative businesses will heighten the in-person retail experience. In the metaverse, the boundaries of creativity are endless. Brands can provide experiences that would be impossible in physical life. For example, why not create a dragon that flies around your store and takes customers on tours of your virtual world? - 3D Commerce
Videos and images might entice in Web 2.0, but user expectations have changed in the metaverse. In a virtual world where 3D avatars replicate individuals, 3D images have become the minimum standard.3D visualizations offer unparalleled customer engagement potential. Whereas a 2D image, or even a video, requires consumers to trust the product, 3D renderings take the mystery out of purchases. Customers can pivot a product to see what it looks like from all angles or use AR to place a 3D scaled image in the physical environment the product will occupy.Operating and interacting in a 3D environment is more intuitive, engaging, and interesting than browsing 2D images online. Customers become impressed and engaged with the technology while feeling more empowered in their purchasing decisions. Shopify found that merchants who add 3D content to their stores see a 94% conversion lift, on average.
- Hyper-personalized experience
The COVID-19 pandemic brought forth a sudden and intense increase in digital lifestyles. Consequently, more customers engaged with online leaders already practicing personalized e-commerce tactics, like individualized discounts. As a result, these experiences became a common consumer demand. Put simply, customer values and expectations are changing. According to McKinsey & Company’s “The Next in Personalization 2021 Report,” 71% of consumers expect companies to create personal interactions, and 76% are frustrated when they don’t. Players who are leaders in personalization tailor offerings and outreach to the right individual at the right moment with the right experiences. In fact, the same report showed that the fastest-growing companies drive 40% of their revenue from personalization compared with slow-growing businesses.”Customers will expect real-time audio and visual communication with friends and brands alike,” Boyd said. “They will expect brands to be omnipresent and their experience in the metaverse to be hyper-personalized. They want memorable and entertaining experiences, even throughout the product-education phase.”Luckily, the tools of the metaverse should help brands keep up. With artificial intelligence (AI) and custom avatars, you can provide any consumer personalized service that makes them feel like they’re having a one-on-one experience. The many new interactions and social considerations will give businesses a unique opportunity to collect new forms of data generated by user interactions.
- Focus on digital goods
Most digital natives consider their virtual identities, represented by customizable avatars, to be a direct extension or mirror of their identity. For these customers, who are poised to dominate the market soon, purchasing a digital T-shirt is as important as buying a physical one. Both items communicate status and satisfy the human need for self-expression.As we mimic our physical lives in the virtual world, digital goods will become more critical. These statements may sound theoretical, but the money in virtual assets is very real: According to BCG, the digital asset total transaction value will range somewhere between $150 billion to $300 billion by 2025. In a 2021 Wunderman Thompson report, 3,011 participants across the United States, UK, and China said they would pay up to $2,000 for a digital handbag. Clearly, customers are willing to spend money on digital assets.The metaverse will foster creativity: In a marketplace that transcends physical limits, why would you offer the same product as everyone else? For example, a car company might create a virtual car that can fly to the moon.
- Stronger community engagement and connection
The metaverse borrows from traditional gaming elements to create communities built around similar interests of areas of exclusivity. These connections transcend physical boundaries. To understand the scale of online socializing, consider that about 60 billion messages are sent daily on Roblox. To engage this consumer base, companies will need to shift e-commerce strategies to align with community engagement and connection values. - Digital Twins: Bridging the physical and virtual
Some experts call the metaverse a “digital twin” of the real world — a term gaining traction in the e-commerce world. Businesses are building digital twin stores of their brick-and-mortar shops or manufacturing plants. As such, businesses are likely to invest as much – or even more – in their digital strategies as they do in their physical stores. In fact, 81% of global consumers polled think that a brand’s digital presence is as important as its in-store presence, according to a 2021 survey by Wunderman Thompson. In some cases, virtual-only stores, like Forever 21 in Roblox, only sell virtual goods. In other scenarios, digital twin stores allow customers to experience and interact with a product before placing an order for its real-life, physical representation. This “experience and buy” sector (instead of “click and buy”) has extended to phone apps that leverage AR and 3D technology to let customers see how products work. For example, Amazon’s shopping app uses AR to place 3D renderings of products in the field of view of a customer’s camera. Other furniture retailers using AR technology include Bob’s Discount Furniture, Ashley Furniture, Macy’s, Ikea, and American Furniture Warehouse.
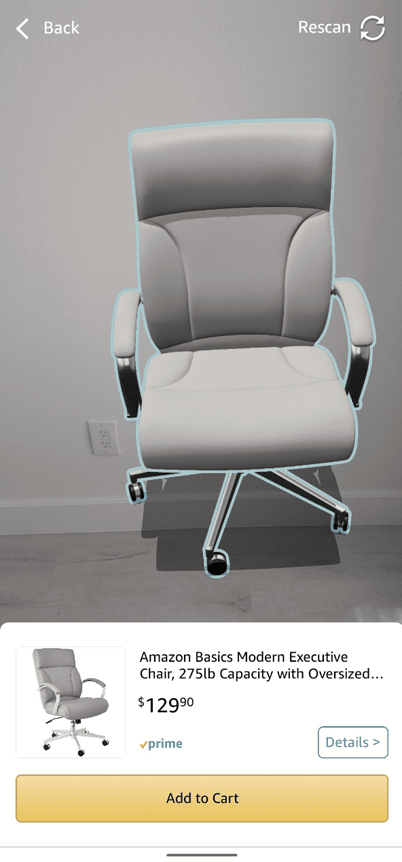

Amazon’s “Explore in Room,” enabled by AR technology, allows users to point their cameras in their home and visualize how 3D models of furniture and other items might look in their space.
- Stronger customer-brand relationships
Online shopping can feel transactional and superficial, with little opportunity for the customers to appreciate the brand. Customers accepted these relationships as a natural limit of Web 2.0, but the tides have shifted in Web3.In the 2017 literature review, “Consumer-Brand Relationships under the Marketing 3.0 Paradigm: A literature review,” published in the Frontiers in Psychology journal, the authors point out that “customers will choose those brands that satisfy their deepest needs.” The authors continue in Marketing 3.0, “Consumers no longer consider only the role of brands as mere identifiers of products, services or companies, but try to go further, basing their brand choices on potential associations and emotional benefits that a specific brand is susceptible to provide them.”Essentially, metaverse commerce allows brands to create experiences for their users and illustrate that brand values align with those of their customers. Brands that don’t embrace this new, value-driven paradigm will lag as more shoppers become dejected and disillusioned with product-centric marketing campaigns. - More brand collaborations
Many businesses are more willing to enter the uncharted territories of metaverse e-commerce with a partner. Along with marketing collaborations, partnerships with technology companies are no longer optional. The problems and hurdles of the metaverse are too big to face alone. Joint investments will increase collective access to the space, benefiting everyone. Finally, because we still don’t have interoperable virtual worlds where users can seamlessly transport from one platform to another, a business hoping to enter the metaverse needs to align itself with a platform. This collaboration requires a company to adopt some community nuances unique to its platform. So far, it seems like innovative brands are more than willing to collaborate: To date, The Sandbox, a popular metaverse platform, has had 200 strategic partnerships. Shared experiences will also create new co-creation opportunities for brands and customers. For example, Coca-Cola partnered with the metaverse platform Fortnite Created to build “Pixel Point” a virtual island where players can engage with Coca-Cola’s new flavor, “Zero Sugar Byte.” The brand markets the flavor as being “born in the metaverse.”
Fortnite user in Coca-Cola’s “Pixel Point” virtual world, housed on Fortnite
- Better customer insights and fewer returns
Metaverse consumers will be more empowered in all their purchasing decisions, thanks to 3D visuals that allow for a complete assessment of a product. As a result, sporadic purchases will decrease substantially. These habits will reduce return rates for physical and digital products, and give businesses more reliable, focused data into customer behavior. - User-generated content
User-generated content (UGC) is the beating heart of the metaverse. Without UGC, the metaverse would be a superficial and static experience rather than dynamic, creative, or immersive.Online habits are changing; people are no longer passive consumers but creative agents curating their virtual identity. When players get involved with the game’s design or create their own quests, spaces, or items, they feel automatically more invested and engaged. This vision differs widely from the passive experiences in Web 2.0. In the metaverse, people want recognition for their creations. Brands can collaborate with content creators to provide AR and VR tools to consumers.Thanks to the blockchain, creators will be able to monetize their work in new ways. A unique transitional experience, “Direct-to-Avatar” (D2A) will emerge as both brands and creators sell their productions exclusively in the virtual world. - Immediate global reach
One of the most interesting and attractive features of the metaverse is its global reach. By 2030, Citi predicts that there could be 5 billion users on the metaverse. From an e-commerce perspective, the opportunities to massively scale and cater to global audiences will provide obvious benefits and challenges. - Higher profitability
According to JP Morgan , the metaverse will culminate in a market opportunity worth more than $1 trillion in annual revenues. Additionally, 42% of business executives believe that the metaverse will be “transformational.”With global audiences, deepened customer relationships, and forecasted global adoption, companies that invest now will certainly benefit from a larger slice of metaverse revenue. Duman, a marketing and CX expert, turns to tried-and-true stats when he thinks about metaverse profit margins. “According to Apple, when users can view furniture in their homes using AR, they are 11 times more likely to purchase it. Thanks to advanced product visualization capabilities in the metaverse, consumers will be able to make better-informed purchasing decisions which would lead to higher profit margins and better sales conversion for brands.” - Potential for higher brand recognition:
Today, we view brands that begin to invest in virtual worlds as innovative and hip. Early adopters will have a chance to define this dynamic space and mold it to their benefit. Just like “Google” is synonymous with search engines and Web 2.0, current big-name brands – and ones we haven’t yet heard of – will gain extraordinary brand recognition as a reward for early investment in the metaverse.
Components of Metaverse E-commerce
Many businesses have already begun to engage in metaverse e-commerce. Successful brands find their metaverse niche. They create revenue streams from immersive experiences and offer NFTs and virtual goods.
Metaverse e-commerce consists of tech, economic, and social components. For example, creators build virtual worlds with 3D visuals. While blockchain powers their economies. Also, these users crave social connections and personalized experiences.
Here are some examples of how brands are engaging in the metaverse today.
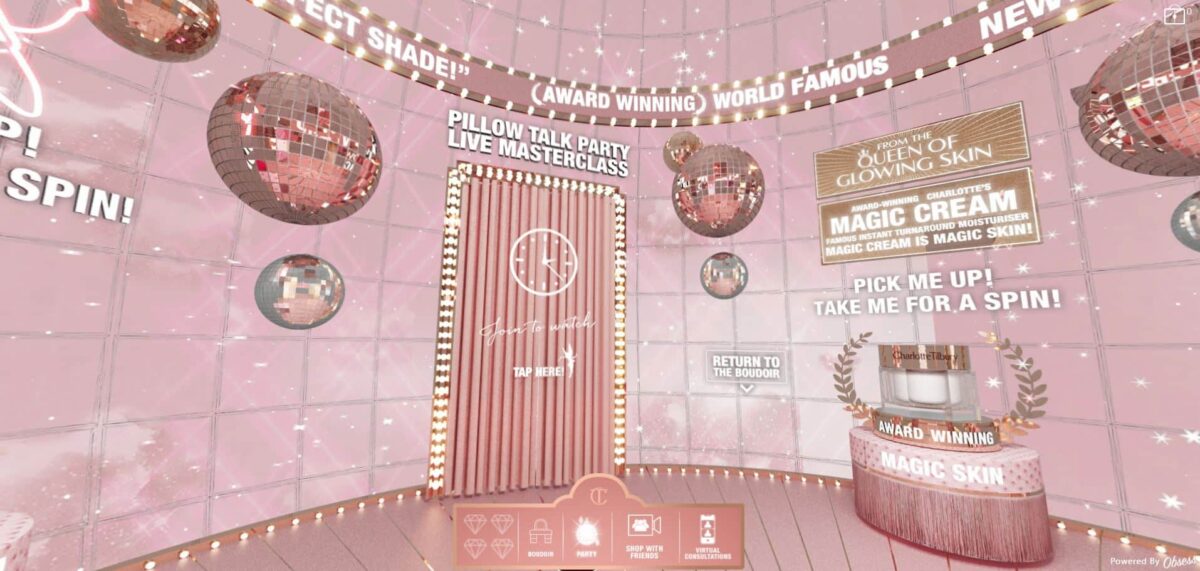
- Charlotte Tilbury Virtual Reality Store
Metaverse elements: Immersive experience, hyper-personalized, virtual products, digital twin store, VR/AR - Metaverse experience: Beauty brand Charlotte Tilbury offers an immersive, virtual store powered by the AR platform Obsess. The brand’s unique approach is the “Shop with Friends” feature. Friends can log on together, in real-time, to shop and interact with one another. Visitors can give tips to friends and interact with virtual stylists. The brand’s omnichannel functionality shows its dedication to digital-first experiences.

Charlotte Tilbury Virtual Reality Store, featuring “Shop with friends,” where you and your friends can shop together in a virtual store.
·
- Forever 21 Virtual Store
Metaverse elements: Immersive experience, gamification, community, virtual products, digital twin store, VR/AR Metaverse experience: In the metaverse platform Roblox, fans can enter the Forever 21 World. Here, you can shop for virtual products for your avatar or socialize in one of the world’s many plazas. The world also centers around the “Top Shop” game, where users create and manage their own store, competing to become the “top shop.” Starting with an empty glass shop, users can expand it and add options like exteriors and architectural themes while performing tasks like stocking inventory and hiring employees. The retailer hopes that by gamifying fashion, users can express their individuality and deepen their relationship with the brand.
User interacts in the Forever 21 Virtual Store on Roblox.
- Jimmy John’s and the Metasandwich
Metaverse elements: Gamification, personalized experience, digital twin store, community, virtual goods, AR/VRMetaverse experience: At Jimmy John’s virtual restaurant on Decentraland, users can submit ingredients for their unique virtual sandwich, which may become the first “Metasandwich.” If their creation wins, Jimmy John’s will serve it on a real menu for a limited time.
Jimmy John’s restaurant on Decentraland where you can build a “Metasandwich.”
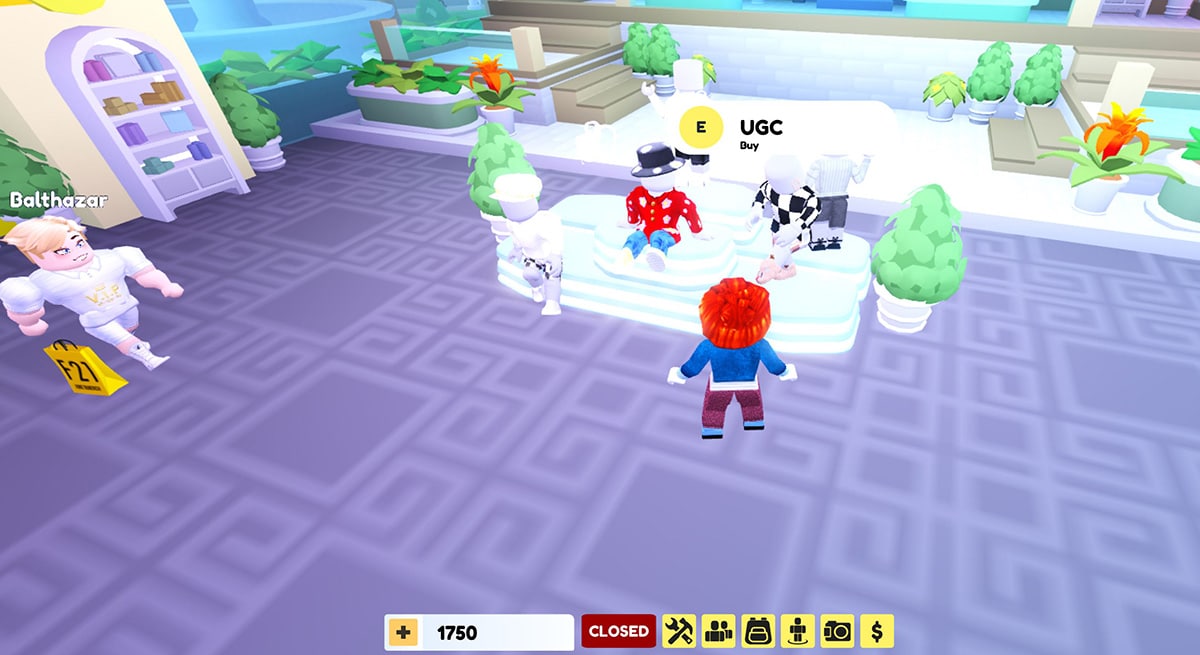
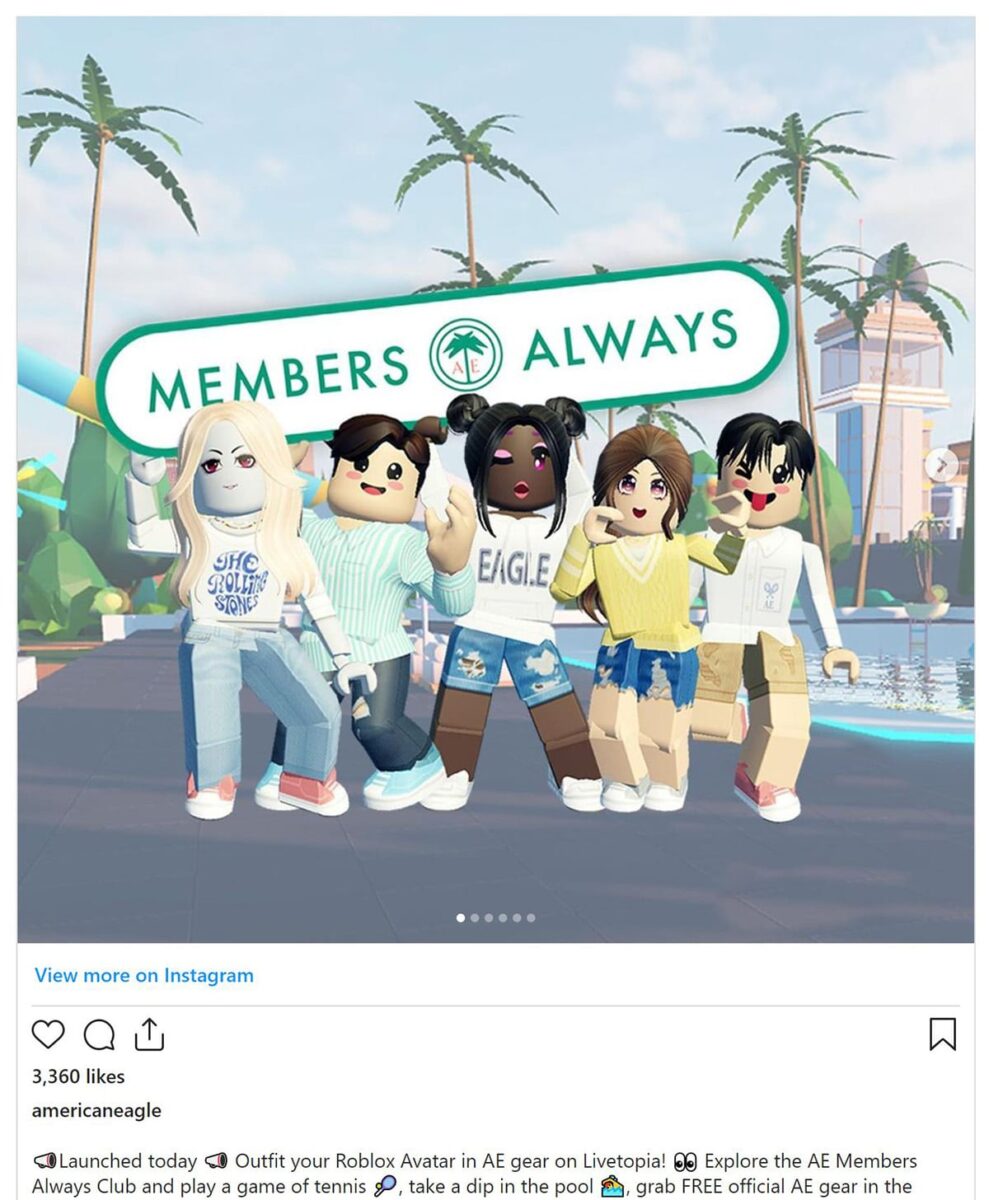
- American Eagle Members Always Campaign
Metaverse elements: Gamification, virtual goods, community, digital twin store, AR/VRMetaverse experience: In American Eagle’s “AE Members Only” world, housed on the virtual Livetopia on Roblox, users can try on some of the 2022 spring collection, collect items, and purchase virtual goods.
American Eagle “Members Always” world
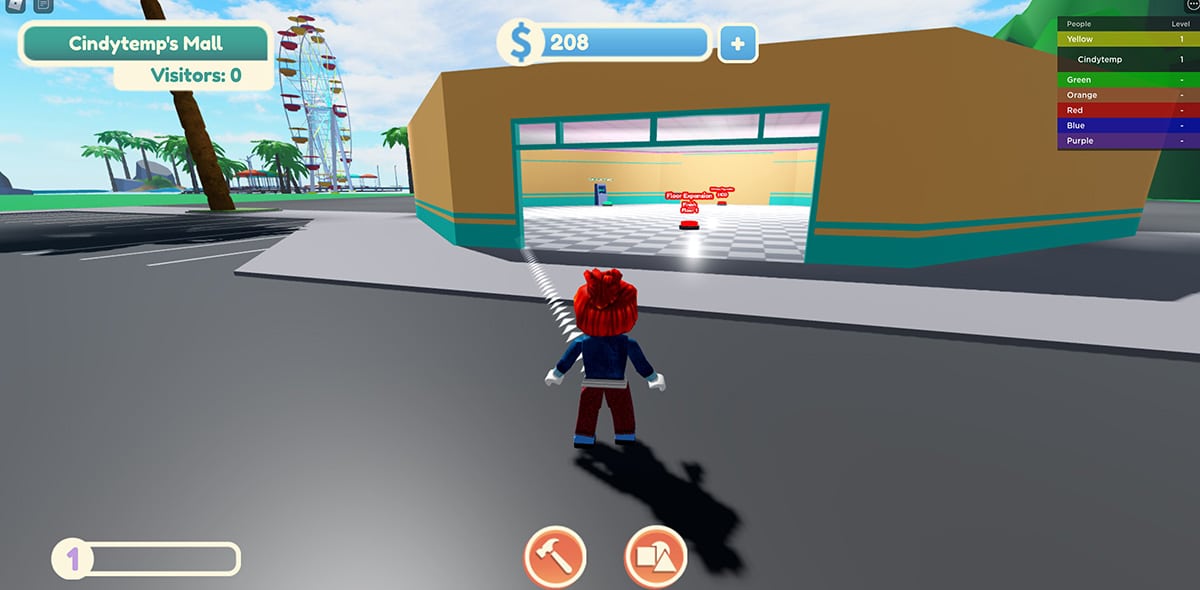
- Pacsun PACWORLD
Metaverse elements: Gamification, virtual goods, hyper-personalized, community, NFTs, AR/VRMetaverse experience: Apparel retailer Pacsun launched PACWORLD on Roblox, where users can create their own “malls” and buy Pacsun apparel. The company also showed its commitment to digital retail by unveiling a set of NFTs called “Pac Mall Rats,” a collection of 300 images that correspond to one of the store’s 300 physical locations.
A user begins to create a mall in PACWORLD
- Hyundai Mobility Adventure
Metaverse elements: Gamification, immersive experience, community, virtual goods Metaverse experience: In “Hyundai Mobility Adventure,” users solve various missions to help citizens in their virtual world and get rewards. Hyundai uses the world to show off their new and future vehicles while deepening relationships with younger customers exploring it.
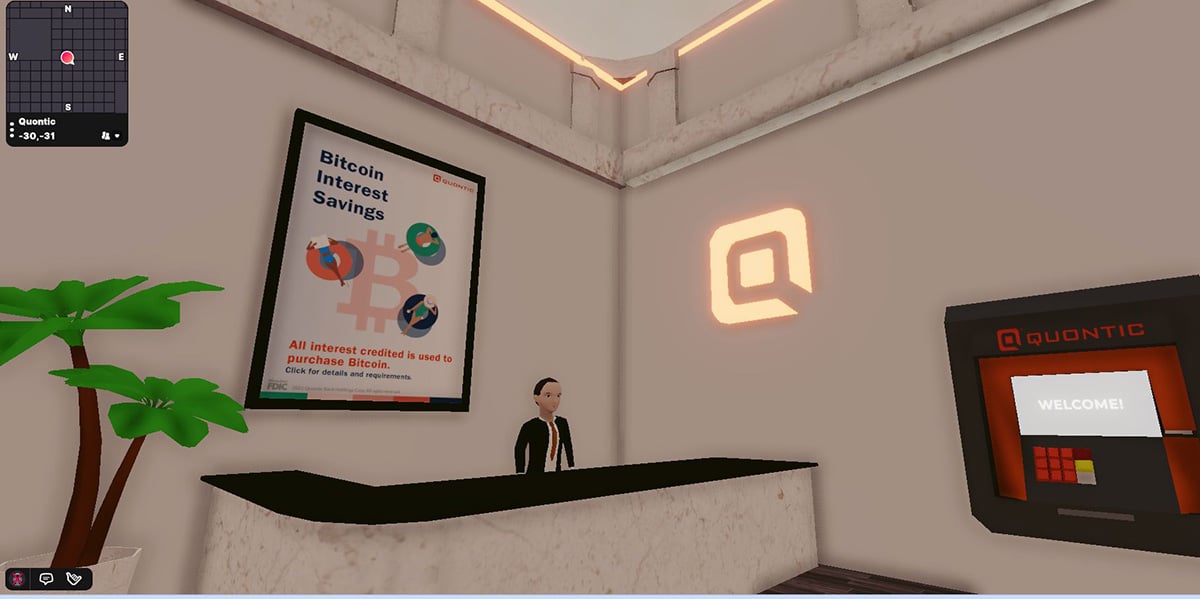
- Quontic Bank in Decentraland
Metaverse elements: Enabling blockchain, digital twin, AR/VRMetaverse experience: Quontic bank opened a virtual post in Decentraland in May 2022. It is the first bank to have an outpost in the metaverse and offer Bitcoin rewards on checking accounts.
Quontic bank in Decentraland
- Hyundai Mobility Adventure
- Nikeland Collection on Roblox
Metaverse elements: Gamification, immersive experience, virtual goods, digital twin stores, celebrity partnerships, community, AR/VR Metaverse experience: Nike has been a leader in the metaverse since it opened up “NIKELAND” on Roblox in late 2021. In “NIKELAND,” users can explore the vast virtual environment, play and invent games, socialize with other users, and purchase digital goods in the showroom. The investment has paid off: Within four months of opening, nearly 7 million people worldwide visited it and made in-game purchases.As a sign of its continual investment in the metaverse, Nike arranged for basketball legend LeBron James to make virtual visits to fans in Roblox. The superstar visited “NIKELAND” and offered basketball lessons through a series of mini-games, all designed to help users up their real-life basketball game. The event was a clever way to promote the sale of Nike’s new “Chosen 1” shoes.
The “NIKELAND” showroom on Roblox.
- Nikeland Collection on Roblox
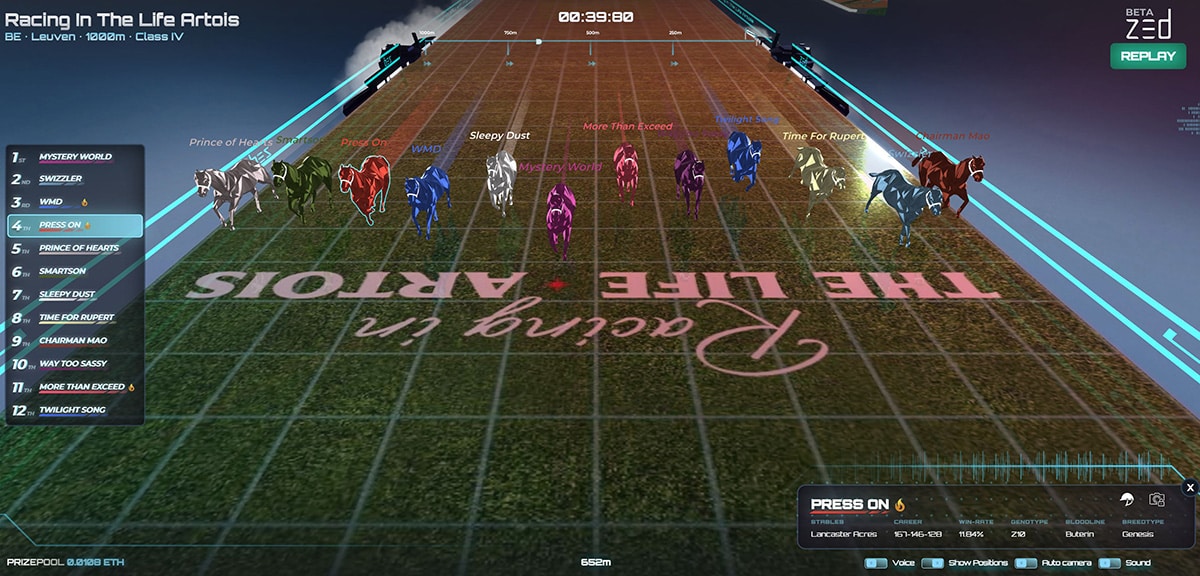
- Stella “Racing in the Life” Artois
Metaverse elements: Gamification, NFTs, virtual products, brand partnerships, community, AR/VRMetaverse experience: Makers of Stella Artois, a famous pilsner beer, partnered with ZED RUN, a digital horse racing game built on the blockchain. The brand created an NFT collection that introduces 50 limited-edition racehorse skins and NFT artwork. Stella Artois also auctioned ten virtual digital racehorses that users can race on a 3D racetrack. Some of the most coveted virtual steeds sell for upwards of $36,000.
Stella Artois teamed up with Zed Run for a horse-racing experience where users can use NFTs to sell and breed digital racehorses
- The Costacos Collection NFTs
Metaverse elements: NFTs, virtual goods, brand partnerships, communityMetaverse experience: John Costacos, renowned pop culture artist, has created a series of NFTs in his Costacos Collection. Recently, the artist partnered with four legendary NFT quarterbacks: Troy Aikman, Warren Moon, Jim McMahon, and Dan Marino. Another Costacos NFT, celebrating Willie Mays, sold for $50,000.
The Costacos Quarterback Legends NFT Collection
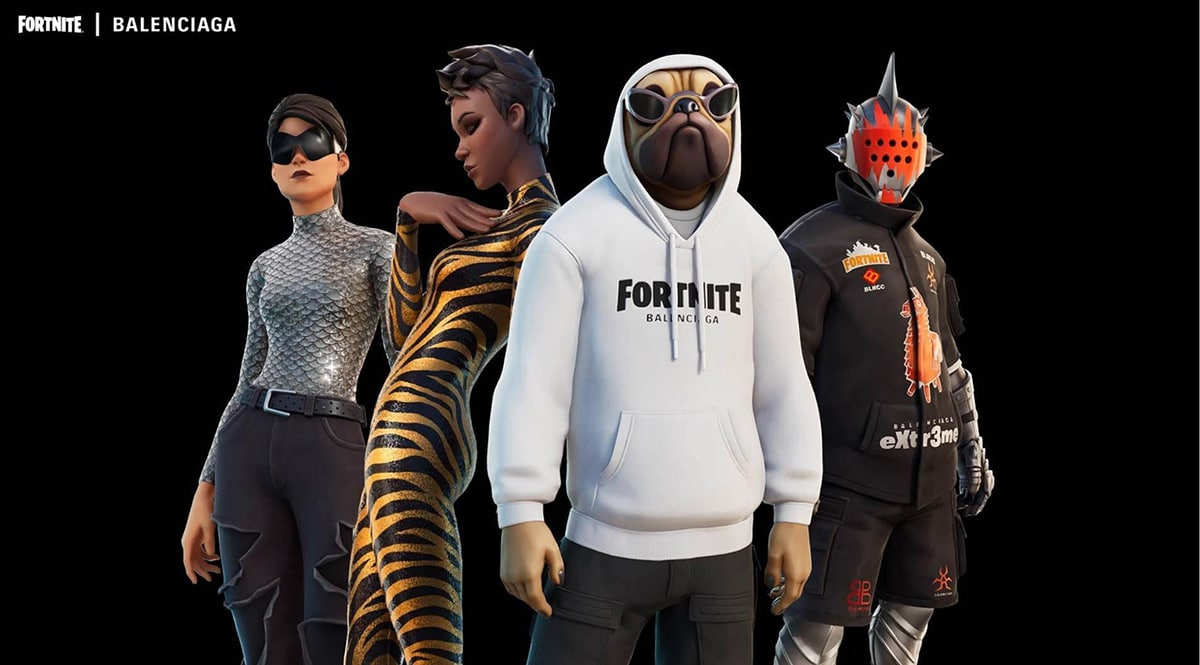
- Balenciaga Avatars
Metaverse elements: Virtual goods, avatars, gamification, brand partnerships, community, AR/VR - Metaverse experience: Fashion house Balenciaga collaborated with Fortnite to provide outfits and accessories for their avatars. The company debuted a “living logbook” inside Balenciaga’s retail store in Fortnite’s Hub to accompany the digital apparel launch. The “logbook” will show the Fortnite community’s fashion on billboards. Balenciaga also sells physical Fortnite apparel online and in their Balenciaga stores.

Fortnite avatars wear Balenciaga apparel.
Examples of Companies Preparing for Metaverse E-commerce
Top brands across industries have joined the metaverse movement. This list includes McDonald’s, Levi’s, CVS, and Disney. With new brands entering daily, the metaverse will soon be a mandatory investment for every serious business.
Big brands like McDonald’s, CVS, Disney, Levi’s, Victoria’s Secret, Dove, and more have all filed trademarks, publicly expressing their intention to enter the metaverse. Clearly, some of the most recognizable brands see the potential of the metaverse and are preparing trademarks for the virtual economy. With trademarks and NFT filings increasing by nearly 100 percent over the past year, entering the metaverse has almost become a requirement for business success.
Here’s a comprehensive list of some top brands preparing for the metaverse, organized by sector.
Beauty and Health Care:
- Johnson and Johnson: The pharmaceutical company has filed trademark applications for NFT versions of “Neutrogena” and “Aveeno” beauty products. The healthcare giant also announced its intent to open a metaverse retail store that offers virtual and physical goods. The public announcement, a witty tweet claiming “dry skin will not be a problem in the metaverse” puts Johnson and Johnson in company with other health and beauty giants, like L’Oréal and CVS. They who filed trademark applications to join the metaverse.
- CVS Health: On February 28, 2022, the company filed a patent to sell virtual goods, NFTs, and provide health care services in the metaverse. CVS plans on focusing on non-emergency medical treatments, like wellness programs and nutrition services that they can deliver in a telehealth, virtual platform setting. With this step, CVS hopes to keep pace with consumers who prefer a digital-first approach.
- L’Oréal: The cosmetic brand will soon offer virtual beauty shops featuring virtual cosmetics, makeup preparations, and perhaps even avatars in the metaverse. In the spring of 2022, the cosmetic giant filed 17 trademark applications that clearly showed their interest in the metaverse.
- Dove: The personal care brand has also filed a trademark application to sell virtual goods and even arrange and host virtual performances.
Fashion:
- SFL Maven: In early spring 2022, the leading luxury goods retailer announced they will partner with MetaSkins Studios to design and create a retail location in Decentraland. The company will sell high-end vintage digital jewelry items for avatar use and will be the first high-end jeweler operating in the Metaverse.
- Victoria’s Secret: The company filed four new trademark applications. It plans to sell “virtual lingerie, footwear, and fashion accessories.”
- Levi’s: The jeans brand has joined Versace, Champion, Wrangle, Hugo Boss, and others in expressing its intention to enter the metaverse. The company filed three trademarks for its name, logo, and brand. Like other fashion retailers, Levi’s will begin by offering NFTs and virtual products sold in digital stores.
Food:
- Tony Roma’s: In May 2022, the restaurant chain announced it filed trademark registrations to join the metaverse. The announcement comes on the heels of the brand’s 50th anniversary. They intend to open virtual restaurants that immerse customers in its history, offer up some secrets to mastering BBQ, and invite users to interact with the executive chef, Bob Gallagher.
- Panda Express: Before you know it, your avatar might be taking a lunch break at the “PANDAVERSE.” Panda Express filed four trademark applications soon after McDonald’s and Panera Bread announced similar intentions to provide virtual stores that blend digital food with home delivery.
- Food coming soon to the metaverse: Other food brands that have publicly announced their metaverse intentions include KFC, Hooters, Taco Bell, Tyson Foods, Chobani, and Burger King.
Entertainment:
- Disney: One of the most recognized global brands has also shown a strong interest in the metaverse. Though the company has yet to file any trademarks, Disney’s CEO, Bob Chapek, confirmed the brand’s interest in connecting their theme parks and streaming service, Disney+, in virtual spaces.
- Tetris: Owners of the iconic video game applied for a trademark to provide NFTs, blockchain software, and virtual entertainment environments.
Along with these corporate giants, other smaller, rising companies have made enormous strides towards the metaverse. Here’s a list of some soon-to-be-known companies flocking towards the metaverse.
- Orange Comet, Inc.:The creative media company announced a partnership with Sid & Marty Krofft Pictures, the creators of popular television programs like “Land of the Lost” and “The Bugaloos.” The company, already famous for its NFT partnership with AMC theaters, will create NFT collectibles that pay homage to iconic shows and characters.
- Nitches, Inc.: In May 2022, the modern clothing line company announced a collaboration with Voodo Fé, a world-famous multimedia artist, to create an exclusive NFT clothing collection. Nitches received a licensing agreement with the Miles Davis family to create streetwear items that celebrate his work. Each item will have a QR code sewn into the clothing to authenticate ownership. Once the owners scan the product, they’ll receive integrated NFT versions of their clothing for digital use and other perks.
These small and big companies also don’t represent the thousands of content creators that will monetize their creations on the metaverse. These include celebrities like Kevin Durant and Billie Eilish, plus famous – and soon-to-be-famous – NFT creators. For example, UFC fighting legend, Amanda Nunes, will partner with The Sports Metaverse to offer fighting classes and personal training at her metaverse gym.
It’s worth noting that companies are also racing ahead to enable the metaverse. Meta (formerly Facebook) has announced its plans to build a supercomputer estimated to be 20 times faster than its current machine. Meta wasn’t shy about its purpose: they hope to use the supercomputer to help build the metaverse and create new AR and AI tools. Apple is poised to enter the market in 2023 with a headset that reaches improved resolution. Fixed (fiber and Wi-Fi) and mobile (5G and 6G) providers, like Verizon, have also begun to innovate to allow for the intense computing power demanded by the metaverse.
How to Prepare for Metaverse E-commerce
To prepare for metaverse e-commerce, establish a team focused on strategy, design, and tech. Then, start investing in 3D, AR, and VR technology to create virtual, visual-rich e-commerce experiences.
Before you jump feet first into the metaverse, take the time to consider your goals. Businesses that hope to make a quick buck will almost certainly be let down. The metaverse will fundamentally shift the way we live. If you plan to enter, you should also plan to stay in it for the longhaul, be ready to experiment and embrace the inevitable failure of being an early mover.
Duman, marketing and CX expert, advises business leaders that “experimentation should be your ultimate goal in the initial metaverse.” He also points out, “Leaders building this new form of commerce will need to think outside-the-box and do more than replicate their retail stores into virtual ones.”
Still, metaverse preparation will be a balance of careful preparation and quick execution. Boyd of TechSparq concurs, “Businesses that have not begun their preparations into the metaverse are already late. Metaverse commerce is happening right now. It will require a massive business transformation to capitalize on the new metrics and advertising opportunities and meet customer expectations.”
Metaverse preparation may sound overwhelming, but you don’t need to take a huge leap forward to make significant strides and position your business well for success. Here’s how you can start preparing for metaverse e-commerce today.
- Research: Start learning about your sector’s technologies, trends, and possible applications. Learning about potential metaverse applications will be extremely valuable as the next generation of experiences unfolds.
- Strategize and build use cases: Brands should understand that they’ll never be creating the perfect metaverse commerce experience for the next five to ten years. Still, the goal should be experimenting and making progress. If you start today, you’ll have a huge competitive advantage in understanding your customer’s behavior in this space and how to build a long-term strategy that puts metaverse commerce at the core of your revenue stream in the long haul.
- Mitigate risk: You will eventually need to accept cryptocurrency and likely offer NFTs, which still carry risk. For example, celebrity Seth Green lost an NFT worth 200k in a phishing scam. The nature of fraud and data security hacking will evolve alongside other metaverse-tech. So, along with strategists and content creators, hire a digital security team that will work to protect your IP and crypto and lawyers to help in case things go south.
Of all the technology to invest in, 3D models represent an obvious first choice. 3D visuals will continue to be the backbone of all immersive content. Plus, 3D technology has been around for a long time, unlike XR, meaning that even small businesses can adopt the technology without breaking the bank.
- Build a 3D talent pool: Creating 3D environments, products, and immersive experience requires a coveted, newly emerging skillset. Investing today in building a robust 3D talent pool will help position you to work in the metaverse while others play catch-up. In short, identify where you expect to compete as an enterprise and then determine which skill gaps prevent you from realizing that vision.
- Experiment in 3D immersive content: Prioritize identifying, acquiring, and developing employees with skills in AR, VR, XR, and AI. This talent pool is small, so companies that don’t compete will fall behind. Make sure your top tech leaders continually research and invest in the latest AR innovations to anticipate new applications.
- Upskill existing employees: Explore upskilling existing employees through vendor-based training in the Web3 and metaverse platforms.
- Develop a library of 3D Assets and virtual goods: Brands that already have a rich library of 3D assets will be able to participate more quickly. An easy way to start is to create 3D renderings of your entire product catalog.
Marxent CEO and Founder Beck Besecker emphasizes the unique value of 3D content. “Investing in 3D is a great way to get started with metaverse technologies that have an immediate application and ROI on existing websites and within mobile commerce experiences,” he said. “It’s the perfect place to start. Having a complete 3D catalog and a pipeline for creating 3D content allows retailers to provide buyable SKUs within rich Web3 content experiences. It’s the perfect place to start.”
How Marxent Helps Companies Conduct 3D Commerce in the Metaverse
Marxent experts have their fingers on the pulse of the metaverse, ensuring that their clients will be ready for e-commerce in the metaverse at all its stages. Marxent can help you transform your catalog into Web3-ready 3D visuals. You won’t just excel in today’s e-commerce ecosystem but will be ready when it is time to invest in metaverse commerce.
3D Cloud by Marxent offers the most comprehensive, elite 3D visualization platform available. It can easily turn your online photos into full-scale, stunning, and realistic 3D visuals. The scalable program means you can manage all your web content, across all your platforms, in one place. Top brands trust Marxent to take their images and bring them to life with award-winning 3D product configurators, 3D room planners, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) solutions. Ready to learn more? Here’s why retailers choose 3D Cloud by Marxent.